Why do some students stay while others leave?
College is an exciting chapter, but for many students, staying in the course isn’t as easy as it seems. Some drop out because of financial struggles, academic pressure, or simply feeling like they don’t belong. Others push through because they find the right support, whether in the form of a great professor, a strong peer network, or academic resources that help them stay on track.
Universities that understand these challenges and proactively address them see higher retention rates and, more importantly, students who feel valued and motivated to succeed.
So, how do institutions create an environment where students want to stay?
Let’s break down what retention is, why it matters, and how universities are making a difference.
Understanding Student Retention
Student retention is a big deal in universities—it’s all about making sure students stick around long enough to finish their degrees.
But what does retention actually mean? And how does it differ from persistence?
Let’s break it down and explore key ideas, to understand what keeps students engaged and on track.
Definition and Meaning
At its core, student retention is about keeping students enrolled from year to year until they graduate. It’s usually measured by the percentage of students who stay at the same institution throughout their academic journey.
Why does this matter? Because high retention rates often signal that students are satisfied, academically successful, and well-supported by their university.
Think of it this way: A university is like a marathon coach. Some students may struggle along the way, but with the right mix of academic support, strong advising, and a sense of belonging, they’re more likely to cross the finish line.
Schools that prioritize retention focus on things like:
- Academic support programs to help students stay on track.
- Community engagement so students feel connected to their peers.
- Personalized advising that addresses individual challenges and goals.
By fostering a supportive environment, universities make it easier for students to navigate their educational journey without feeling lost or overwhelmed.
Tinto’s Model Explained
One of the most well-known frameworks for understanding retention is Tinto’s Model of Student Retention, developed by Vincent Tinto.
He argues that students are more likely to stay in school if they feel a sense of integration—both academically and socially.
Imagine a student who joins a study group, attends campus events, and has a mentor who checks in regularly. That student is far more likely to persist than one who feels isolated and disconnected from campus life.
According to Tinto, successful integration happens in two ways:
-
Academic integration: When students feel they are succeeding in their coursework and getting the right academic support.
-
Social integration: When they build friendships, engage in campus activities, and feel like they belong.
For college registrars, this model is a useful roadmap. The more universities invest in engagement—through orientation programs, peer mentorship, and campus involvement—the better their retention outcomes.
A student who feels like part of a community is far less likely to drop out.
Student Persistence vs. Retention
The terms persistence and retention get tossed around a lot, but they don’t mean the same thing. Think of it like this:
- Retention = The university’s ability to keep a student enrolled at the same institution.
- Persistence = The student’s personal effort to complete their degree, even if they transfer schools.
A student who leaves one university but enrolls elsewhere is still persisting—they just aren’t being retained by their original institution.
This distinction matters because it shifts the focus from just keeping students enrolled to actually supporting them in reaching their long-term educational goals.
For example, a registrar might notice a pattern: students transferring due to financial hardship, academic struggles, or feeling disconnected from campus life. Knowing this, the institution can take proactive steps—offering emergency financial aid, academic coaching, or stronger first-year engagement programs—to not only boost retention but also help students persist in their education, wherever they end up.
Strategic Framework for Retention
Retention isn’t about forcing students to stay—it’s about creating an experience where they want to stay.
Building a solid student retention framework isn’t just about numbers—it involves creating an environment where students feel supported, engaged, and equipped to succeed.
This means developing smart plans, using proven strategies, and ensuring academic advising is more than just a check-in.

Developing a Student Retention Plan
A well-crafted student retention plan starts with understanding the unique needs and challenges of your student body.
Why do students leave? What helps them thrive? The answers to these questions can shape targeted initiatives to boost retention.
Begin by collecting and analyzing data—look at dropout trends, academic struggles, and student feedback. Numbers tell part of the story, but conversations with students fill in the gaps.
What’s causing them to disengage? Are financial pressures, academic difficulties, or a lack of community playing a role? Once you pinpoint the biggest barriers, you can create tailored solutions.
Engage key stakeholders—faculty, students, and administration—to ensure a well-rounded approach. Retention isn’t just one department’s job; it requires collaboration across campus.
Set clear, measurable goals and regularly track progress. A retention plan isn’t static—it should evolve based on student demographics, feedback, and emerging challenges. If students change, your strategies should too.
Retention Strategies in Higher Education
Effective retention strategies blend technology with personal engagement. Universities that rely solely on data miss a crucial element—human connection.
-
Early warning systems: Use data to flag at-risk students early. If a student’s grades start slipping or they stop attending classes, timely intervention can make all the difference.
-
Financial support options: Money problems are one of the biggest reasons students drop out. Offer flexible payment plans, emergency grants, and clear guidance on scholarships and financial aid.
-
Building a strong campus community: Students who feel like they belong are more likely to stay. Encourage participation in clubs, mentorship programs, and campus events. A sense of connection can be just as important as academic success.
-
Addressing Barriers in Course Registration: Every semester, many students are blocked from enrolling due to registration holds. Registrars can review hold policies to ensure only essential holds prevent registration. Universities can also create support teams to help students clear holds before they impact enrollment.
-
Improving Course Scheduling for Retention: Poor course scheduling—like limited sections or awkward class times—can delay graduation and raise tuition costs. Registrars can prevent this by using enrollment data to offer high-demand courses at times that fit student schedules, not just faculty preferences.
Think about it—when students feel invisible, they disengage. When they feel seen, heard, and valued, they stay. Retention isn’t just about preventing dropouts; it’s about making students want to stay.
Advising for Success
Academic advising isn’t just about picking classes—it’s a critical component of student success and retention. A good advisor can be the difference between a student who feels lost and one who feels empowered.
-
Personalized guidance matters: Advisors should go beyond academic planning and address personal challenges that may impact a student’s success. A student struggling with mental health or financial stress isn’t just an academic case—they’re a person who needs support.
-
Frequent check-ins build trust: Encourage regular advisor-advisee meetings, not just at the start of each semester. A strong relationship between students and advisors leads to better retention outcomes.
-
Training advisors for success: Advisors need the right tools to be effective. Ongoing training in communication, problem-solving, and student engagement ensures they’re equipped to handle complex student issues.
Leverage technology to streamline advising—automated scheduling, student progress tracking, and digital check-ins help maintain continuity, even if an advisor changes. Students should never feel like they’re starting over every time they meet someone new.
When done right, academic advising isn’t just a retention strategy—it’s a lifeline for students navigating their college journey.
Metrics and Measurement
When it comes to student retention, numbers tell a story.
Universities track retention rates to understand how well they’re keeping students engaged and enrolled. But measuring retention isn’t just about crunching numbers—it’s about identifying trends, spotting problem areas, and using data to improve student success.
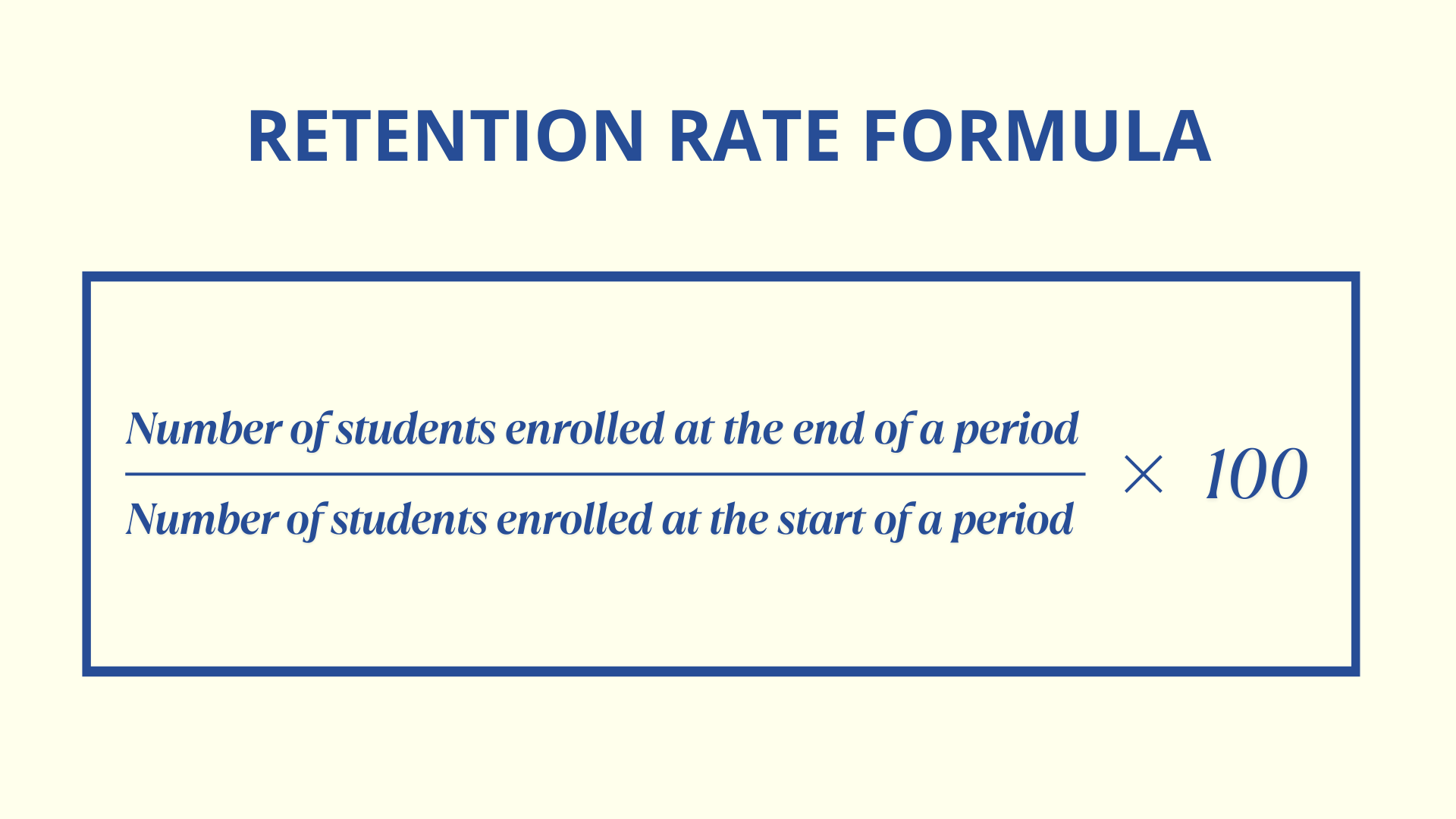
The Retention Rate Formula
To measure retention effectively, universities use a simple yet powerful formula:
Retention Rate = (Number of students enrolled at the end of a period/Number of students enrolled at the start of the period)×100
This formula gives a clear percentage of how many students remain enrolled from one academic period to the next.
For example, if a school starts with 1,000 students and 750 remain at the end of the term, the retention rate would be 75%.
But looking at the number alone isn’t enough. The key is to dig deeper—who is leaving, and why? Are certain demographics struggling more than others? Are financial concerns driving students away? By analyzing these patterns, universities can take targeted actions to improve student retention.
Understanding Retention Rates
A university’s retention rate is one of the clearest indicators of how well it supports its students.
High retention rates suggest students feel connected, academically supported, and financially secure—factors that ultimately lead to higher graduation rates. On the other hand, low retention rates can signal underlying issues, such as lack of engagement, academic struggles, or financial barriers.
For registrars, tracking these rates is essential. Why? Because retention affects everything—from institutional reputation to funding and enrollment numbers.
A university known for keeping students engaged is more likely to attract new applicants, while schools with high dropout rates may struggle to maintain a strong reputation.
Major factors which influence retention are:
-
Academic support – Tutoring, mentoring, and advising programs help students navigate challenges.
-
Campus engagement – A sense of belonging keeps students motivated and committed.
-
Financial aid accessibility – Money problems shouldn’t be the reason a student drops out.
By monitoring these elements closely, universities can adjust their strategies to improve retention.
For instance, if data shows that first-year students are struggling, investing in stronger orientation programs or peer mentorship could make a big difference.
Data & Institutional Research
University student retention isn’t just about keeping students enrolled—it’s about understanding why they leave and acting on it.
But if retention data is scattered across departments, with inconsistent definitions of withdrawals, transfers, and persistence, it becomes hard to find real solutions.
Registrars play a critical role in ensuring clean, standardized retention data that accurately reflects student experiences. Without it, universities risk basing retention strategies on assumptions instead of facts.
By collaborating with institutional research teams, registrars can turn raw data into action.
Are students leaving after their first year? Are certain majors seeing higher dropout rates? With accurate reporting, patterns emerge, and universities can address issues before they escalate.
Retention isn’t just about tracking numbers—it’s about making sure those numbers lead to better decisions.
Retention Theories and Models
Over the years, researchers have developed various theories and models to analyze the factors that influence student retention.
These insights help universities design effective strategies to keep students engaged and on track to graduation.
Tinto’s Student Integration Model
Vincent Tinto’s model emphasizes the importance of academic and social integration in student retention.
According to this framework, a student’s commitment to their educational goals and their integration into the institution’s academic and social systems are pivotal. Factors such as teaching quality, student support services, and social engagement opportunities play significant roles in influencing a student’s decision to persist or withdraw.
Bean and Metzner’s Model of Student Attrition
This model focuses on non-traditional students, highlighting the impact of environmental factors alongside academic variables.
It suggests that external elements like financial challenges, family responsibilities, and employment commitments can significantly affect a student’s persistence, sometimes even more than academic factors.
Understanding these influences is crucial for institutions to develop effective support systems tailored to diverse student populations.
Pascarella’s General Model for Assessing Change
Pascarella’s model integrates academic offerings with students’ pre-college academic and social experiences.
It underscores the importance of creating an institutional environment that is attractive and conducive to interaction among students, thereby fostering a sense of community and belonging that supports retention.
Veenstra’s Model for Freshman Engineering Retention
Specifically addressing retention in engineering programs, the Veenstra model identifies nine pillars critical to student success: high school academic achievement, quantitative skills, study habits, commitment to career and educational goals, confidence in quantitative skills, commitment to the enrolled college, financial needs, family support, and social engagement.
This comprehensive approach highlights the multifaceted nature of retention and the need for targeted interventions.
Learning Communities Model
Learning communities involve structuring curricular experiences to promote integration and interaction among students and faculty.
Models include linked courses, learning clusters, and freshman interest groups, all designed to enhance academic and social engagement. Participation in learning communities has been associated with higher GPAs, increased retention rates, and a stronger sense of belonging among students.
Improvement and Intervention Strategies
To improve retention, universities need proactive strategies that address student challenges before they lead to dropouts.
Let’s explore how early identification and tailored interventions can make a difference.
Increasing Retention
To boost student retention, the first step is to identify at-risk students early.
This means keeping an eye on academic performance, attendance patterns, and engagement levels. A student who suddenly stops showing up to class? That’s a red flag.
An early warning system—such as automated alerts for low grades or missed assignments—can help faculty and advisors step in before students fall too far behind.
But monitoring alone isn’t enough. Students need a sense of belonging. Universities should encourage participation in student organizations, mentorship programs, and faculty-led discussions to help students build connections. When students feel like they’re part of something bigger, they’re far more likely to stay.
And let’s not forget support services. Some students leave due to academic struggles, while others face personal or financial barriers. Offer access to tutoring and mentoring programs, counseling services and financial aid options proactively. Go to students with these solutions rather than waiting on them to come to you.
All these elements work together to reduce dropout rates and create a learning environment where students can thrive.
Retention Intervention Methods
Sometimes, even the best students struggle—and that’s where intervention strategies come in.
The key? Personalized support. Every student has different needs, and a one-size-fits-all approach won’t work. Instead, universities should focus on tailored academic advising that considers each student’s unique goals, struggles, and learning styles.
Another effective method? Data-driven insights. By analyzing real-time data—like sudden drops in attendance or lower-than-usual test scores—advisors can step in before issues spiral.
Beyond academics, fostering an inclusive campus community helps, too. Students who feel seen and accepted—regardless of background, identity, or financial status—are more likely to persist in their studies. That’s why universities should create spaces that celebrate diversity, inclusion, and open dialogue.
Finally, financial barriers remain one of the biggest obstacles to retention. Students who are worried about paying for tuition can’t focus fully on their education. Universities should make it easy to access scholarships, grants, and work-study opportunities—and communicate these options clearly.
By focusing on both academic and social support, universities can create an environment where students don’t just stay—they succeed.
Institutional Factors and Policies
A supportive campus environment and well-designed policies play a huge role in keeping students enrolled.
Universities that invest in thoughtful retention strategies create a space where students feel connected, supported, and motivated to complete their degrees.
But how exactly do institutional factors and policies impact student retention? Let’s break it down.
Role of Institutional Factors
A university isn’t just a place to take classes—it’s a community. And that community plays a big role in whether students stay or leave.
Everything from the campus atmosphere to class sizes to student support services influences retention. If students feel welcome, engaged, and encouraged, they’re far more likely to stick around.
Take peer relationships, for example. A student who builds strong friendships and connections on campus is less likely to drop out than one who feels isolated. The same goes for faculty and staff—having approachable professors and supportive advisors can make all the difference.
Another key factor? Proactive intervention. Universities that train staff to recognize early warning signs—like declining grades or frequent absences—can step in before a student decides to leave. Something as simple as a check-in email or a meeting with an advisor can be enough to help a struggling student get back on track.
The Impact of Withdrawal & Leave of Absence Policies
Not every student who withdraws wants to leave for good.
Many just need time—a semester off for financial reasons, a family emergency, or personal struggles. But without a structured leave of absence policy, students may feel like leaving is their only option, making it harder for them to return.
Universities can prevent this by offering a formal leave policy that keeps students connected—allowing them to retain email access, advising support, and an easy re-enrollment process.
Understanding why students leave is just as important as helping them return. A simple withdrawal survey before students officially drop out can provide key insights—was it financial, academic, or personal? If a trend emerges, the university can take action.
Creating Effective Retention Policies
Good retention policies aren’t just about rules—they’re about support. Universities need policies that foster engagement, connection, and academic success.
Some of the most effective ones include:
-
Early Academic Intervention Programs – Offering tutoring, study groups, or skills workshops can help students who are struggling before they fall too far behind.
-
Mentorship Initiatives – Pairing new students with mentors—whether faculty or upperclassmen—builds a sense of belonging and guidance.
-
Financial Support – Scholarships, emergency grants, and flexible payment plans help remove financial barriers that often lead to dropout decisions.
Money stress is one of the biggest reasons students leave college. Imagine being passionate about your studies but constantly worrying about tuition—it’s exhausting. Universities that prioritize financial aid and clear, accessible funding options set their students up for success.
Finally, policies shouldn’t be static. Engaging with students, gathering feedback, and adapting policies to meet their evolving needs ensures they remain effective. After all, the goal isn’t just keeping students enrolled—it’s helping them thrive.
Special Considerations in Student Retention
When it comes to keeping students enrolled, it’s important to understand the unique challenges that impact different student groups.
Two key areas that demand attention are supporting minority students and learning from past retention trends to make smarter decisions. Let’s dive deeper.
Retention of Minority Students
For minority students, college can sometimes feel like stepping into unfamiliar territory.
Cultural differences, language barriers, and a sense of isolation can create roadblocks that make it harder for them to stay and thrive. If students don’t feel like they belong, they’re more likely to leave.
So, what can universities do?
-
Foster a sense of community. Mentorship programs, cultural clubs, and events that celebrate diverse backgrounds can make a huge difference. Students are more likely to stay when they see themselves reflected in campus life.
-
Train faculty and staff in cultural competency. A simple, well-timed conversation with a professor who understands a student’s struggles can change everything.
-
Ease financial burdens. Scholarships geared toward minority students help level the playing field. Academic support, such as tutoring and counseling services, also ensures they don’t fall behind.
By addressing these challenges, universities don’t just improve retention—they build a richer, more inclusive academic environment where all students can thrive.
Prior Student Retention and Its Meaning
You can’t fix what you don’t understand. That’s why looking at past student retention trends is crucial—it tells you what’s working, what’s not, and where to focus your efforts.
Think of it like this: if students keep leaving for the same reasons year after year, ignoring that pattern is like driving with a flat tire and hoping it magically inflates.
-
Analyze historical data. What trends stand out? Are certain majors seeing higher dropout rates? Is there a dip in retention after the first year?
-
Identify key factors. Are students leaving due to academic struggles, lack of engagement, or financial difficulties?
-
Use the data to predict future trends. If you see warning signs early, you can put the right support systems in place before students even think about leaving.
Retention is about more than just numbers. It’s about understanding why students stay and why they go—and then using that knowledge to create a better experience for everyone.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Boosting student retention isn’t just about having good intentions—it’s about using proven strategies and learning from institutions that are doing it right.
Some universities have cracked the code on keeping students engaged and enrolled, and their successes offer valuable lessons. Let’s look at what’s working.
Successful Retention Programs
Some of the most effective student retention programs start with one simple concept: spot struggling students early and give them the support they need before they slip through the cracks.
-
Targeted advisement support is one strategy that has made a big impact. Schools like the University of Maine use data-driven advising to identify students who may be at risk of dropping out. Advisors then step in with personalized guidance, whether it’s help with coursework, career planning, or even emotional support. When students feel seen and supported, they’re far more likely to stay.
-
Peer mentoring programs are another retention booster. Students helping students—it’s that simple. Many colleges pair first-year students with upper-year mentors who can answer questions, offer encouragement, and share their own experiences. The result? Freshmen feel more connected and confident navigating their college journey.
-
First-year experience courses help set students up for long-term success. Universities that offer structured programs focused on study skills, time management, and academic planning see higher retention rates. CampusGroups highlights this as a key factor in helping students transition smoothly into university life. Think of it like giving students a roadmap so they don’t get lost in the chaos of their first year.
When universities invest in guidance, mentorship, and structured support, students aren’t just more likely to stay—they’re more likely to thrive.
Lessons from High Retention Institutions
What do colleges with high retention rates have in common? A strong sense of community.
-
Campus involvement is key. Universities with high retention rates encourage students to join clubs, organizations, and activities to help them feel like they belong. When students build friendships and engage with campus life, they’re not just earning a degree—they’re becoming part of something bigger. And that sense of belonging keeps them coming back.
-
Flexibility matters. Life doesn’t pause for school, and high-retention institutions recognize that. Many offer online courses, hybrid models, and flexible scheduling to accommodate students balancing jobs, families, and other responsibilities. A student who doesn’t have to choose between their education and their paycheck? That’s a student who stays enrolled.
-
Mental health and wellness support are non-negotiable. Stress, anxiety, and personal struggles can derail even the most motivated students. Universities that prioritize accessible counseling services, stress management resources, and wellness programs create an environment where students feel supported—both academically and personally. When students know help is available, they’re far less likely to walk away.
The bottom line? Universities that invest in community, flexibility, and student well-being don’t just hold onto students; they help them succeed.
And that’s what higher education is all about.
Supporting Student Retention with EduTranscript
Student retention is a complex issue influenced by academic, financial, and administrative factors. While coursework and financial aid often take center stage, efficient access to academic records plays a critical role in keeping students on track toward graduation.
When students face difficulties obtaining transcripts, verifying credits, or understanding their academic progress, they can experience delays in course registration, financial aid processing, or transfer applications.
These roadblocks can lead to frustration and disengagement, increasing the likelihood that students pause or abandon their education.
For college registrars, the challenge is balancing accuracy, compliance, and efficiency while managing thousands of transcript requests.
EduTranscript helps streamline this process, ensuring that students have timely access to their records, reducing unnecessary administrative hurdles that can slow down their academic journey.
Key Ways EduTranscript Helps Registrars Support Student Retention
Eliminating Transcript Processing Delays
Students frequently need transcripts for advising, internship applications, financial aid verification, and transfers. If processing takes too long, students may face unnecessary barriers that complicate their academic progress.
EduTranscript automates transcript generation and delivery, significantly reducing wait times. This ensures that students receive their records promptly, allowing them to make time-sensitive academic and career decisions without administrative delays.
Simplifying Credit Transfer & Articulation
Transferring between institutions or changing majors often requires a credit evaluation process that can be time-consuming and unclear. If students don’t have a clear understanding of how their existing credits apply, they may experience delays in registering for courses, which can extend their time to graduation.
EduTranscript provides structured articulation agreements and automated credit evaluations, allowing students and advisors to quickly assess how completed coursework applies to their degree requirements. By reducing uncertainty and minimizing unnecessary coursework repetition, institutions can help students stay on track without extending their academic timeline.
Providing 24/7 Student Self-Service Access
Many registrar offices operate within standard business hours, but students often need transcript access outside of that timeframe for job applications, graduate school submissions, or financial aid processing. Limited access can create unnecessary frustration and administrative backlogs.
EduTranscript’s self-service portal allows students to access their transcripts anytime, without requiring staff intervention. This improves operational efficiency for registrars while ensuring that students can retrieve critical academic records when they need them.
Why This Matters
When students encounter administrative obstacles—whether it’s waiting for transcripts, dealing with unclear credit transfer policies, or struggling to access their records—they can become disengaged.
While these challenges alone may not cause students to drop out, they contribute to unnecessary delays and frustrations that make academic progress harder than it needs to be.
By simplifying these processes, institutions can create a more supportive academic environment, helping students stay enrolled and complete their degrees on time.
Conclusion
At its core, university student retention isn’t just about policies or programs—it’s about reducing friction in a student’s academic journey.
A registrar’s role is pivotal in keeping these roadblocks to a minimum, ensuring students have the support they need to move forward. The more streamlined and responsive your processes are, the easier it is to keep students on track.
Small operational improvements can make a big difference. Automating transcript requests, simplifying transfer credit evaluations, and offering self-service access to records help students make informed decisions without frustration. These changes don’t just ease the workload for your office—they contribute to a campus culture where students feel supported rather than stuck in red tape.
When students can focus on their education instead of paperwork, they’re more likely to persist and graduate.
That’s where EduTranscript comes in. It helps registrars eliminate transcript delays, simplify credit transfers, and provide students with 24/7 access to their records—all with minimal administrative burden. By making these processes smoother, you’re not just improving efficiency; you’re actively supporting student retention.
If you’re interested in seeing how EduTranscript can work for your institution, book a demo call today and explore a smarter way to manage academic records.
.png)
 Author :
Author :