Whether you’re a student submitting an application, a professor grading assignments, or an administrator handling enrollment, your data is constantly being collected, processed, and stored. That’s where GDPR in education comes into play.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) establishes strict rules on how educational institutions handle personal information, ensuring that it’s collected responsibly, stored securely, and used transparently. Without proper safeguards, institutions risk data breaches, legal penalties, and, most importantly, a loss of trust from their students and staff. Compliance isn’t just a legal necessity, it’s a fundamental part of ethical data management.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know, from student rights to institutional responsibilities, making GDPR easy to understand for anyone in the education sector.
Understanding GDPR in the Educational Context
GDPR isn’t just a set of legal rules, it’s a framework designed to keep personal information secure. Schools and universities are data controllers, meaning they’re responsible for handling student and staff data safely.
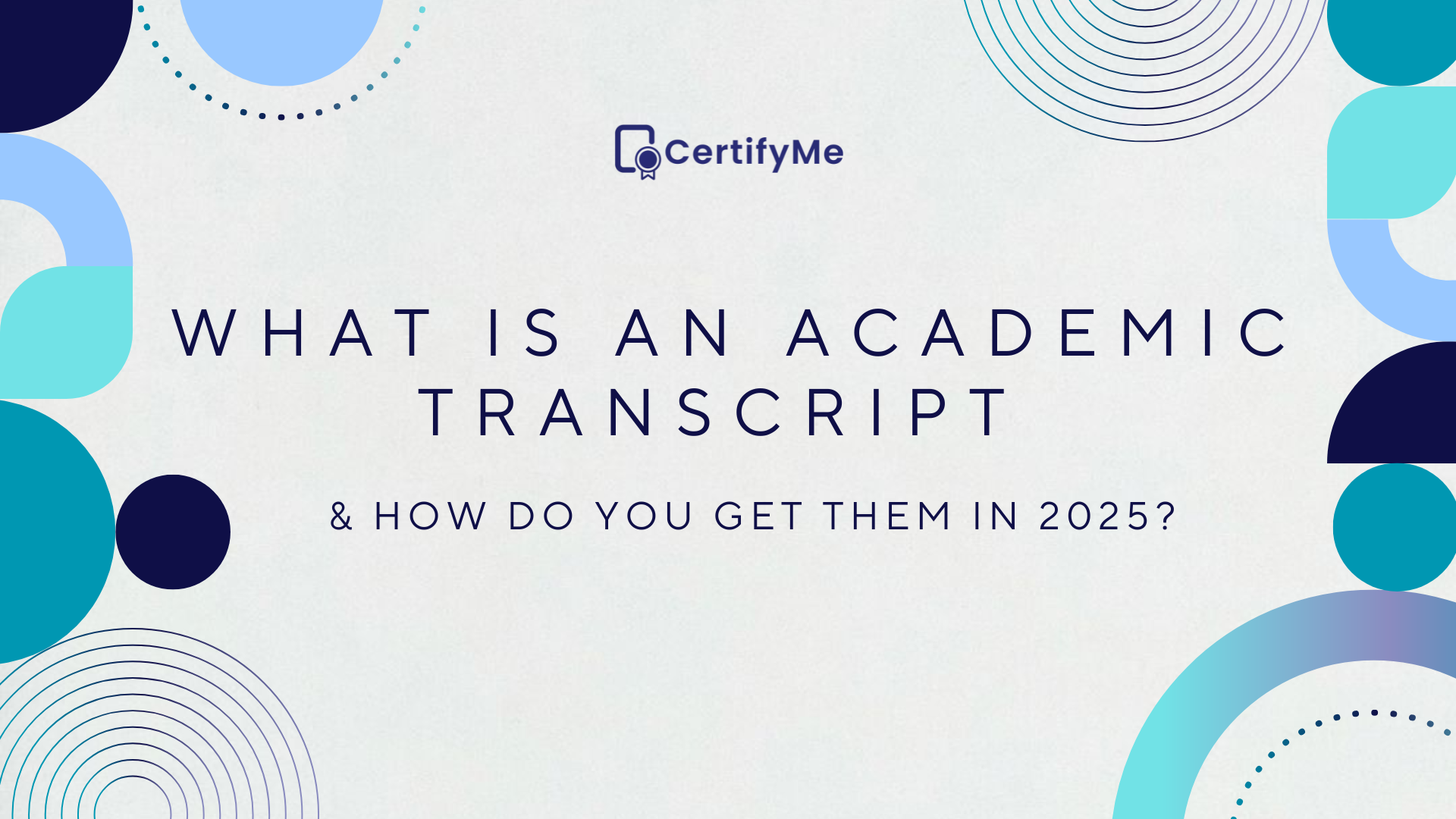
The foundation of GDPR rests on several core principles:
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Institutions must collect and process data in a lawful and transparent manner. No hidden agendas.
- Purpose Limitation: Data should only be used for specific educational purposes—no repurposing without consent.
- Data Minimization: Only collect the information you truly need. Less data means less risk in case of a breach.
- Accuracy: Institutions must keep data up-to-date and allow individuals to correct any errors.
- Storage Limitation: Personal data shouldn’t be kept indefinitely. Universities must establish clear data retention policies.
Mastering these principles helps educational institutions stay compliant while also fostering a culture of responsibility when handling personal data.
GDPR Meaning and Objectives in Education
At its core, GDPR compliance in higher education ensures that students, faculty, and staff have control over their personal data.
Universities store everything from student transcripts to financial records—GDPR makes sure this data is handled with care.
Educational institutions aren’t just passive data holders—they are data controllers. This means they have a legal and ethical obligation to collect, process, and store personal information in a way that aligns with GDPR principles. Whether it’s ensuring that students give clear consent before their data is used, maintaining accurate and up-to-date records, or putting strict data security measures in place, compliance is not optional.
Here’s how GDPR protects personal information in education:
-
Enhanced Protection: Schools and universities must take extra steps to secure sensitive information, reducing the risk of data leaks.
-
Empowering Individuals: Students and staff can request access to their personal data or ask for it to be deleted.
-
Clear Responsibilities: Educational institutions must designate staff to oversee GDPR compliance, ensuring proper data management.
-
Informed Consent: Schools can’t just collect data freely—they need explicit permission from students or their guardians.
With these objectives in mind, GDPR for education providers isn’t just a regulation—it’s a commitment to ethical data handling.
GDPR Compliance Strategies for Educational Institutions
Ensuring GDPR compliance in higher education isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s about establishing clear processes for protecting data.
Universities and schools handle everything from student enrollment records to research participant data, making them prime targets for data breaches. Without clear strategies in place, institutions risk legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of trust from students and staff.
To stay compliant, schools must adopt a proactive approach to data protection, focusing on structured assessments, designated oversight, and continuous staff training.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
One way institutions can manage risks is by conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), a structured process that helps institutions identify, evaluate, and minimize data security risks before they become problems. Think of it like a routine health check-up for your data practices.
Steps to perform a DPIA:
-
Identify what data is collected and why.
-
Evaluate whether collecting this data is necessary.
-
Assess the potential risks and who might be affected.
-
Plan measures to minimize risks, such as encryption or restricted access.
Performing a DPIA shows a proactive approach to GDPR compliance, helping institutions stay ahead of potential data issues.
Institutions that neglect this step often find themselves struggling with unforeseen compliance issues down the line.
Role of Data Protection Officers (DPOs)
To ensure compliance, universities often appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)—a go-to expert for all things data security.
While some universities treat this as a formality, having a well-trained DPO is crucial for managing data security effectively.
A DPO’s responsibilities include:
- Advising institutions on their GDPR obligations.
- Monitoring compliance and reporting breaches.
- Conducting GDPR in education training for staff.
- Acting as a contact point for students with data concerns.
Without a competent DPO, universities risk non-compliance, which can lead to costly fines, legal battles, and reputational harm.
Investing in a skilled DPO ensures that GDPR is not just a policy on paper but an active part of the institution’s culture.

Strengthening Internal Data Security Measures
Beyond assessments and oversight, educational institutions must take direct action to secure personal data.
This means implementing multi-layered security measures, such as:
-
Data encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Two-factor authentication (2FA) for faculty and staff accounts.
-
Regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities.
-
Access controls that limit data handling to authorized personnel only.
Even the best policies mean nothing if staff and students aren’t educated about safe data practices.
Regular training sessions, phishing simulations, and internal audits ensure that everyone understands their role in protecting sensitive information. After all, compliance isn’t just about rules—it’s about building a culture where data privacy is a shared responsibility.
GDPR and eDiscovery
Educational institutions often need to retrieve and review digital records for legal or academic disputes.
eDiscovery, the process of searching electronic records for relevant data, must align with GDPR guidelines:
-
Schools must only access and process necessary data for legal proceedings.
-
If student or staff data is involved, institutions need to justify why it’s being reviewed.
-
Data must be handled securely and not stored longer than needed.
Balancing legal obligations and privacy rights requires careful documentation and adherence to GDPR principles.
GDPR Training and Awareness in Education
Understanding GDPR for education providers starts with proper training. Without awareness, even the best policies are useless.
Compliance isn’t just the responsibility of a Data Protection Officer (DPO)—it’s something every educator, administrator, and student needs to understand.
A lack of training and awareness is one of the biggest reasons data breaches happen. Whether it’s a professor accidentally emailing grades to the wrong student or an administrator storing sensitive records on an unsecured device, human errors are often the weakest link in data protection. That’s why consistent, practical training programs are essential.
Building an Effective GDPR Training Program
A strong GDPR training program should be more than just a one-time workshop—it needs to be ongoing, interactive, and relevant to daily tasks.
To ensure compliance, institutions should:
-
Offer online GDPR in education training programs.
-
Use interactive formats like quizzes and case studies.
-
Regularly update materials as regulations evolve.
By making training engaging and practical, universities increase compliance and reduce risk, ensuring that data protection becomes second nature to everyone on campus.
Engaging Educators and Staff
A major challenge is getting staff to take GDPR seriously. Make it relatable—use real-world examples of data breaches and their consequences.
Encourage an open dialogue. Let staff ask questions and share concerns. A culture of GDPR awareness helps prevent mistakes that could lead to data breaches.
To engage educators and staff, institutions should:
-
Use real-life examples of GDPR violations and their consequences.
-
Encourage open discussions where faculty and staff can ask GDPR-related questions.
-
Appoint GDPR champions within different departments to promote best practices.
-
Simulate phishing attacks and other cyber threats to test awareness.
A culture of GDPR awareness goes beyond formal training. It’s about making privacy and security a natural part of everyday conversations.
Institutions that foster this mindset don’t just comply with GDPR—they create an environment where students, faculty, and staff trust that their personal data is handled with care.
GDPR Education Training
Training should cover both legal obligations and practical steps for data protection.
Institutions should:
-
Provide mandatory GDPR education training for faculty and staff handling student data.
-
Use real-world case studies to illustrate the consequences of data breaches.
-
Offer refreshers and updates as GDPR evolves.
Educators don’t need to be legal experts, but they must understand how to handle student information responsibly in day-to-day interactions.
GDPR and Higher Education Institutions
GDPR and higher education institutions face unique challenges, especially when dealing with international students and cross-border data transfers.
A failure to comply doesn’t just mean legal penalties; it can erode trust among students and faculty, damage institutional reputation, and even lead to lawsuits.
For universities, GDPR compliance isn’t just a regulatory requirement; it’s a commitment to ethical data management and digital security.
Challenges and Best Practices
Unlike businesses, universities often operate in a decentralized manner, with multiple departments handling data independently.
Admissions, financial aid, IT, research centers—all have their own data systems and workflows, making compliance complex. Ensuring GDPR compliance in higher education requires a structured approach to managing data responsibly across all departments.
Here are some common challenges universities face and best practices to overcome them:
- Training Staff Consistently
-
Challenge: Many university staff members aren’t aware of GDPR’s implications on their daily tasks.
-
Best Practice: Conduct mandatory GDPR training for all faculty, administrators, and IT personnel, ensuring they understand their roles in data protection.
-
- Obtaining Clear Consent from Students
-
Challenge: Universities collect a wide range of student data—from application details to medical records—but often fail to obtain explicit, informed consent.
-
Best Practice: Clearly state what data is collected, why, and how it will be used in student agreements and online forms. Ensure that students have the option to withdraw consent where applicable.
-
- Keeping Thorough Records of Data Processing Activities
-
Challenge: Universities often struggle with tracking and documenting how personal data is processed, making it difficult to prove compliance.
-
Best Practice: Implement centralized record-keeping systems that log who accesses data, why it’s accessed, and where it’s stored. Conduct regular audits to ensure all departments comply.
-
By addressing these challenges head-on, universities can create a structured, proactive approach to GDPR compliance protecting both students’ rights and the institution’s integrity.
International Data Transfers and Student Privacy
Many universities work with global partners, raising questions about data transfers. Under GDPR, any transfer of personal data outside the European Economic Area (EEA) must meet strict protection standards.
GDPR requires institutions to:
-
Verify that international partners have adequate data protection measures.
-
Use Standard Contractual Clauses(SCCs) when sharing data outside the EU.
-
Clearly inform students about how their data is handled across borders.
The key takeaway?
International collaborations don’t have to be a GDPR nightmare as long as universities take a proactive approach to privacy and security, ensuring compliance every step of the way.
Data Rights and Responsibilities in Education
Education is more than just lectures and assignments—it’s a constant exchange of information between students, faculty, and administrative staff. But who controls this data?
Under GDPR, students and staff have clearly defined data rights, while educational institutions must uphold strict responsibilities when handling personal information.
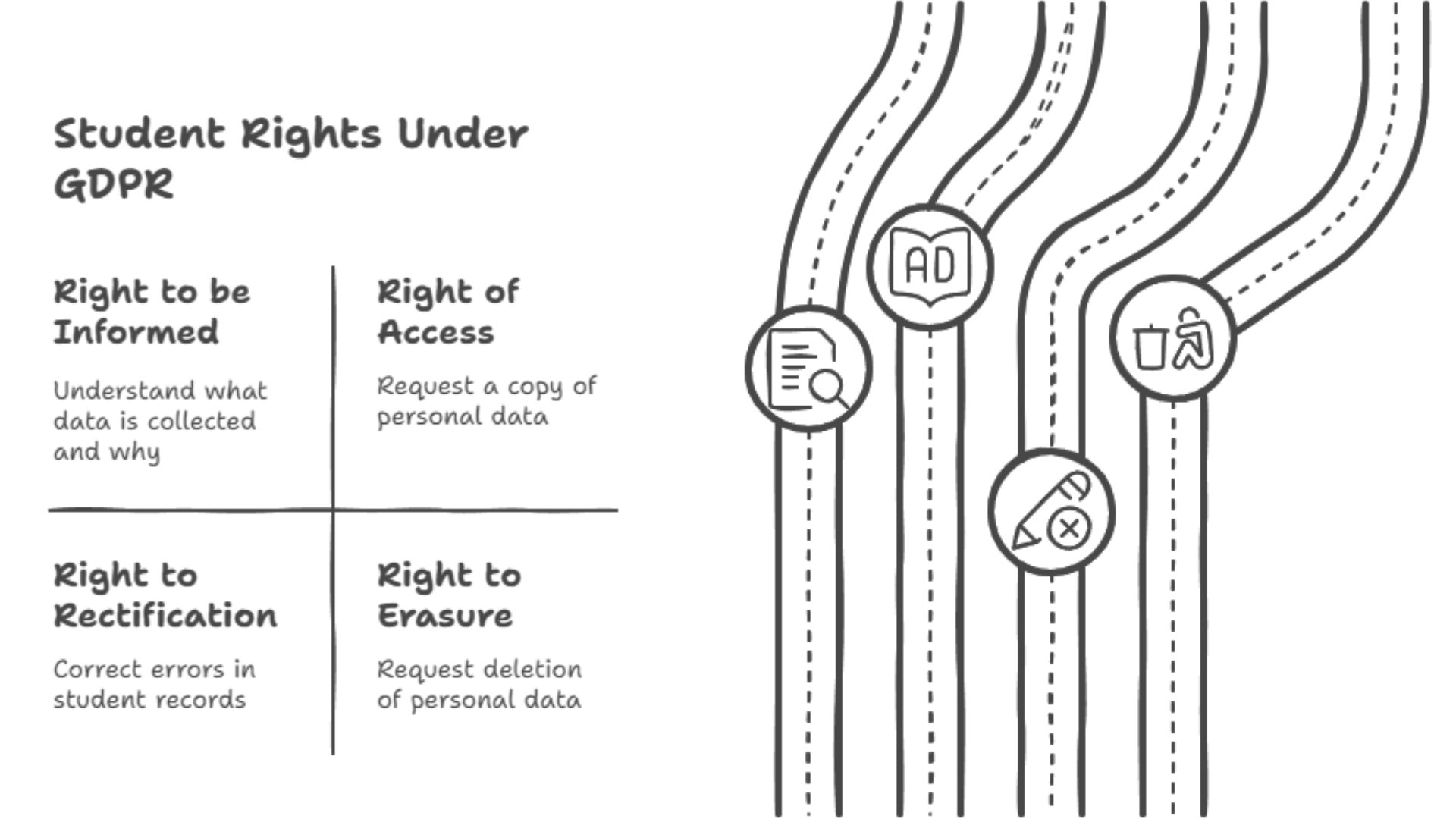
Students’ Rights under GDPR
Students aren’t just passive data subjects; they have legal rights over their personal information.
Universities must be transparent about what data they collect and give students the ability to access, modify, or even delete their information in certain cases.
If you are a student, here’s what you should know:
-
Right to be Informed: Schools must explain what data they collect and why.
-
Right of Access: You can request a copy of your personal data.
-
Right to Rectification: Found an error in your student records? You have the right to correct it.
-
Right to Erasure: In some cases, you can request that your data be deleted.
Understanding these rights isn’t just about legal protections, it’s about ensuring students have control over their own digital identities in an era where data is more valuable than ever.
Educational Providers’ Responsibilities
While students have rights, universities and schools have obligations to keep that data safe, secure, and legally compliant.
Educational institutions function as data controllers, meaning they decide how and why personal data is processed which comes with a heavy responsibility.
Schools and universities must:
-
Establish clear data protection policies.
-
Implement strong security measures to prevent breaches.
-
Train staff to ensure they understand GDPR compliance in higher education.
-
Report any data breaches promptly.
GDPR and School Records
Student records, including grades, attendance, and disciplinary actions, fall under GDPR protection.
Schools must:
-
Ensure only authorized personnel can access these records.
-
Allow students to request copies of their records (right of access).
-
Correct errors upon request (right to rectification).
GDPR Education Data
Institutions collect vast amounts of education data for analytics and decision-making.
GDPR ensures this data is used ethically by requiring:
-
Anonymization of student performance reports when possible.
-
Minimal data retention, ensuring records aren’t stored indefinitely.
-
Transparency—students should know how their data is used in research or administrative decisions.
By enforcing these protections, GDPR ensures that education data is used responsibly while respecting individual privacy rights.
GDPR and School Photos
Taking and sharing student photos is common in schools, but GDPR sets clear rules on when and how these images can be used.
Schools must:
-
Obtain explicit consent from parents (for minors) or students (if over 18) before publishing photos online or in promotional materials.
-
Clearly state the purpose of collecting and using images—whether for yearbooks, social media, or ID cards.
-
Allow individuals to withdraw consent at any time, ensuring their images are deleted if requested.
If an institution fails to comply, even a simple class photo could lead to legal issues. Schools must handle visual data with the same care as other personal information.
GDPR and Related Regulations
While GDPR focuses on personal data, the ePrivacy Directive specifically regulates electronic communications.
This impacts:
-
School websites and cookies—institutions must obtain consent before tracking student behavior online.
-
Emails and messaging platforms—schools must ensure that student and staff communications remain private and secure.
Together, GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive provide a comprehensive framework for protecting personal data in educational settings.
Simplify GDPR Compliance for Student Records with EduTranscript
When it comes to handling student records, GDPR isn’t just another policy — it’s a daily responsibility. Universities deal with sensitive personal data like transcripts, grades, and enrollment records, and managing all this manually can be overwhelming.
One missed step — an unsecured email, a lost file, or an unlogged data request — could lead to serious compliance issues, frustrated students, or even fines.
That’s where EduTranscript steps in. It’s built to simplify data security and take the stress out of compliance for both faculty and administrators.
Here’s how EduTranscript helps universities stay ahead of GDPR challenges:
-
Built-In GDPR Compliance: Every transcript issued through EduTranscript is designed to meet GDPR standards by default — and the platform stays updated to reflect future compliance changes.
-
Encrypted, Tamper-Proof Documents: Transcripts are protected with cryptographic signatures and ID-based tagging, reducing fraud and securing personal data.
-
End-to-End Encryption: From storage to delivery, EduTranscript uses encryption to protect personal data during transmission, ensuring transcripts are secure when sent to students, evaluators, or stored in the system.
-
Clear Data Retention and Expiry Settings: EduTranscript allows universities to define how long transcripts are stored or accessible, aligning with GDPR’s “storage limitation” principle to prevent holding personal data longer than necessary.
-
Simplified Consent Management: Before sharing transcripts with third parties (like employers or credential evaluators), EduTranscript ensures clear consent is obtained from the student, helping universities easily prove compliance.
-
Controlled Access: Only authorized staff can view, edit, or share student records, cutting down the risk of accidental exposure.
-
Audit Trails: Every action — from creation to delivery — is logged and traceable, making GDPR reporting clear and simple.
By reducing manual tasks and creating a clear, secure flow for transcript management, EduTranscript helps universities meet GDPR requirements with confidence — while making the entire process faster and more student-friendly.
Conclusion
When institutions prioritize data protection, they don’t just avoid legal trouble; they create a safer, more ethical learning environment for everyone. After all, no one wants to worry about their private information ending up in the wrong hands.
For students and staff, understanding your rights under GDPR isn’t just a legal formality—it’s an essential step in protecting your personal information. Whether you’re requesting access to your records, asking for corrections, or even opting out of certain data collection practices, you have more control than you might think.
On the other hand, university administrators must ensure that policies are clear, training is effective, and data protection measures are actually enforced, not just written down. GDPR compliance in higher education isn’t a one-time task; it’s an ongoing commitment to responsible data management.
If you’re looking for a smarter way to handle student records while staying GDPR-compliant, EduTranscript is worth checking out.
With EduTranscript, universities can automate and streamline their GDPR compliance efforts for academic transcripts and other student records. The platform protects sensitive student data, simplifies verification and consent processes, and allows registrars to manage transcript requests efficiently — all while reducing administrative workload.
Want to see how it works?
Book a demo call today and explore how EduTranscript can make data protection easier for your institution.
.png)
 Author :
Author :